What Is Headless CMS SEO?
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, the term “Headless CMS” has gained significant traction. As a digital marketer, understanding what Headless CMS SEO entails is crucial for optimizing your online presence. A Headless CMS, unlike traditional systems, decouples the content repository (“body”) from the presentation layer (“head”). This separation allows for greater flexibility in delivering content across various platforms and devices.
Headless CMS SEO focuses on optimizing this unique architecture to ensure that search engines can effectively crawl and index the content delivered through APIs. Unlike traditional CMSs, where SEO strategies are often built into the CMS infrastructure, a Headless CMS requires custom strategies to manage metadata, URLs, and other SEO elements. The flexibility of a Headless CMS can be both an opportunity and a challenge for SEO experts.
The primary benefit of using a Headless CMS for SEO is its ability to deliver content faster and more efficiently. By leveraging APIs, you can maintain a high-performance website that meets user expectations, which is a crucial factor in SEO rankings. However, this advantage comes with its own set of challenges, which we will explore further in the following sections.
🤔 Why Is SEO in Headless CMS Challenging?
Because the front-end is decoupled, SEO responsibilities shift from the CMS to developers and content strategists. Common pitfalls include:
| Issue | SEO Impact |
| Client-side rendering (CSR) | Search engines may not fully crawl JavaScript-heavy pages |
| Missing meta tags | Dynamic pages might lack unique titles/descriptions |
| Poor URL structure | Auto-generated or non-semantic URLs hurt rankings |
| Slow load times | Unoptimized front-end = bad Core Web Vitals |
| No built-in SEO features | Unlike WordPress (with Yoast), headless CMSs don’t auto-generate sitemaps or robots.txt |
✅ How to Do SEO Right in a Headless CMS (Best Practices)
1. Use Server-Side Rendering (SSR) or Static Site Generation (SSG)
- Frameworks like Next.js, Nuxt.js, or Gatsby pre-render pages on the server or at build time.
- Ensures content is immediately visible to search engine crawlers (like Googlebot).
- 🔧 Critical for B2B sites with dynamic product pages or gated content.
2. Dynamically Generate Meta Tags
- Use front-end frameworks to inject unique title tags, meta descriptions, Open Graph, and Twitter cards per page—based on CMS content.
- Example (Next.js):jsx
- 1234<Head> <title>{page.title} | Your B2B Brand</title> <meta name=”description” content={page.metaDescription} /></Head>
3. Implement Clean, SEO-Friendly URLs
- Structure URLs logically:
✅/solutions/erp-software-india
❌/page?id=123
4. Generate XML Sitemaps & robots.txt
- Use tools like next-sitemap (for Next.js) to auto-generate sitemaps from your CMS content.
- Submit to Google Search Console.
5. Optimize Core Web Vitals
- Compress images (use Next.js Image or Cloudinary).
- Minimize JavaScript bundles.
- Use CDNs (e.g., Vercel, Cloudflare) for fast global delivery—key for Indian users in tier-2/3 cities.
6. Add Structured Data (Schema Markup)
- Enhance visibility with Product, Organization, FAQ, or Breadcrumb schema.
- Can be dynamically injected based on content type from the headless CMS.
7. Ensure Crawlability & Indexing
- Test pages with Google’s URL Inspection Tool.
- Avoid blocking crawlers via
robots.txtornoindextags accidentally.
🌟 Advantages of Headless CMS for B2B SEO (When Done Right)
| Benefit | Why it Matters |
| Faster sites | Better rankings + user experience (critical for SaaS/product demos) |
| Omnichannel content | Same content powers web, mobile, apps—consistent messaging |
| Developer flexibility | Build custom SEO features (e.g., dynamic filters for product catalogs) |
| Scalability | Handle high-traffic campaigns (e.g., product launches in India) without CMS bloat |
⚠️ Common Mistake in India
Many Indian B2B tech startups adopt headless CMS for speed and flexibility—but launch without SSR, resulting in empty pages for Googlebot and zero organic traffic.
🚨 Always test your headless site with “View Page Source”—if content isn’t there, Google likely can’t see it either.
✅ Tools to Support Headless CMS SEO
- Next.js (with SSG/SSR) – Most popular for B2B
- Google Search Console – Monitor indexing
- Lighthouse / PageSpeed Insights – Audit performance
- Screaming Frog – Crawl JavaScript-rendered sites
- Ahrefs / SEMrush – Track rankings and technical issues
Final Thought:
Headless CMS isn’t bad for SEO—it’s just different.
With the right architecture (SSR/SSG) and SEO discipline, headless can outperform traditional CMS platforms—especially for agile B2B companies in India scaling globally.
Need help auditing your headless B2B site for SEO? Share your tech stack (e.g., “Sanity + Next.js”), and I’ll suggest a checklist!
The Pros and Cons of Headless CMS for SEO
Every technology has its strengths and weaknesses, and Headless CMS is no exception. Understanding these pros and cons will help you make an informed decision about whether a Headless CMS is right for your SEO strategy.
Pros:
- Flexibility and Customization: Headless CMS allows for complete control over how content is presented, enabling highly customized user experiences that can improve engagement and SEO performance.
- Performance Optimization: By serving content through APIs, Headless CMSs can significantly improve site speed, a critical factor in SEO.
- Omnichannel Content Delivery: Content can be seamlessly delivered across various platforms, from websites to mobile apps, enhancing your brand’s reach and consistency.
Cons:
- Technical Complexity: Implementing a Headless CMS requires technical expertise, which can be a barrier for marketers without a deep technical background.
- SEO Tools Compatibility: Many traditional SEO tools may not be directly compatible with a Headless CMS, requiring additional customization.
- Potential for Increased Costs: Due to the need for specialized development and maintenance, using a Headless CMS can be more costly than a traditional CMS.
Balancing these pros and cons is essential when considering a Headless CMS for your SEO needs. While the potential for enhanced performance and flexibility is alluring, the technical requirements and costs must also be taken into account.
Is Headless CMS Bad for SEO? Common Misconceptions
A prevalent misconception is that Headless CMS is inherently bad for SEO. This belief often stems from misunderstandings about how Headless CMS functions and its impact on SEO practices.
Firstly, some marketers assume that because a Headless CMS separates content management from the presentation layer, it inherently lacks SEO capabilities. However, this is far from the truth. While Headless CMSs do require a different approach to SEO, they are not disadvantageous by nature. In fact, with the correct implementation, they can offer superior SEO performance due to faster load times and enhanced user experiences.
Another common misconception is that search engines cannot effectively crawl content delivered via APIs. While this presents a challenge, it is not insurmountable. By implementing server-side rendering or utilizing prerendering services, content can be made accessible to search engines, thus maintaining SEO integrity.
Further on, Is Headless CMS Bad for SEO?
No, a headless CMS is not inherently bad for SEO—in fact, when implemented properly, it can support or even enhance SEO performance. However, there are important considerations to ensure SEO isn’t negatively impacted.
Why Headless CMS Can Be Great for SEO:
- Performance Optimization
Headless architectures often use modern frontend frameworks (like Next.js, Nuxt.js, or SvelteKit) that support static site generation (SSG) or server-side rendering (SSR), both of which deliver fast, pre-rendered HTML to search engines—ideal for SEO. - Flexibility & Control
Developers have full control over markup, meta tags, structured data, and other on-page SEO elements without being constrained by a monolithic CMS theme or template. - Scalability & Speed
Decoupling the frontend from the backend allows for optimized content delivery via CDNs, improving page load times—a key SEO ranking factor. - Omnichannel Content Delivery
Content can be reused across web, mobile, voice, and other platforms while maintaining semantic HTML structure for search engines.
Potential SEO Pitfalls (and How to Avoid Them):
- Client-Side Rendering (CSR) Without SSR/SSG
If your frontend relies solely on JavaScript to render content (e.g., plain React or Vue apps), search engine crawlers may struggle to index content properly.
✅ Fix: Use SSR, SSG, or hybrid rendering (e.g., Next.js withgetStaticPropsorgetServerSideProps). - Poor URL Structure or Missing Metadata
Without a built-in routing or SEO management system (common in traditional CMSs like WordPress), developers must manually handle canonical URLs, meta titles/descriptions, Open Graph tags, etc.
✅ Fix: Implement a robust SEO component or library (e.g.,next-seo,vue-meta) and enforce content modeling that includes SEO fields. - Missing XML Sitemaps or Robots.txt
Headless setups don’t auto-generate these.
✅ Fix: Generate and serve these files programmatically or via your hosting platform. - Lack of Built-in SEO Tools
Traditional CMSs offer plugins (like Yoast for WordPress) that guide content creators. Headless CMSs typically don’t.
✅ Fix: Choose a headless CMS with strong SEO field support (e.g., Contentful, Sanity, or Strapi with custom plugins), or build internal validation/guidance for editors.
Best Practices for SEO with a Headless CMS:
- Use SSR or SSG for public-facing pages.
- Ensure semantic HTML and proper heading hierarchy.
- Implement structured data (Schema.org) for rich snippets.
- Optimize image delivery (use
srcset, lazy loading, modern formats like WebP/AVIF). - Monitor indexing via Google Search Console.
- Maintain clean, descriptive URLs.
Advanced SEO strategies for headless WordPress sites
Advanced SEO strategies for headless WordPress sites require a deliberate, developer-driven approach—since you’ve decoupled WordPress (used only as a content backend) from the frontend (e.g., built with Next.js, Nuxt, or SvelteKit), many traditional WordPress SEO tools no longer apply directly.
However, this architecture offers powerful opportunities for superior SEO when implemented correctly. Below are advanced, actionable strategies tailored specifically for headless WordPress setups.
🔍 1. Ensure Full Crawlability & Indexability
Problem:
Google and other crawlers must be able to render and index your content—especially if using JavaScript-heavy frontends.
Solutions:
- ✅ Use SSR (Server-Side Rendering) or SSG (Static Site Generation)
Frameworks like Next.js (withgetStaticProps/getServerSideProps) or Nuxt.js (withnuxt generateor SSR mode) deliver fully rendered HTML—ideal for SEO. - ✅ Test with Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool
Verify that Google sees the same content as users. Use “Live URL” vs “Indexed” comparisons. - ✅ Avoid CSR-only (Client-Side Rendering) for public pages
Pure React/Vue apps without SSR/SSG may delay or prevent content indexing.
💡 Pro Tip: Use dynamic rendering (e.g., via middleware or edge functions) for bots if SSR isn’t feasible—but this is a fallback, not a best practice.
🏷️ 2. Dynamic, Structured Meta Tags & Schema
Problem:
Meta titles, descriptions, Open Graph, and structured data must be generated per page from WordPress content.
Solutions:
- ✅ Expose SEO fields in WordPress REST API
Use plugins like:- WP REST API Controller (to expose ACF/Yoast fields)
- Yoast SEO REST API (to access Yoast’s title, meta, focus keyphrase)
- Or create a custom REST endpoint that returns full SEO metadata.
- ✅ Map WordPress SEO data to frontend components
Example (Next.js): jsx
- 12345678<Head> <title>{post.yoast_title || post.title.rendered}</title> <meta name=”description” content={post.yoast_meta_desc || excerpt} /> <meta property=”og:title” content={post.yoast_og_title} /> <script type=”application/ld+json”> {JSON.stringify(generateArticleSchema(post))} </script></Head>
- ✅ Automate Schema.org markup
Generate Article, Organization, BreadcrumbList, or FAQPage schemas based on post type and custom fields.
🗺️ 3. Automated Sitemap & robots.txt Generation
Problem:
Headless frontends don’t auto-generate sitemaps or robots directives.
Solutions:
- ✅ Generate sitemaps at build time (SSG) or on-demand (SSR):
- Fetch all public post URLs from WordPress REST API (
/wp/v2/posts,/wp/v2/pages) - Create
sitemap.xmlprogrammatically (e.g., usingnext-sitemapin Next.js) - Submit to Google Search Console
- Fetch all public post URLs from WordPress REST API (
- ✅ Serve a dynamic
robots.txt
Use API routes or serverless functions: js
- 123456789⌄// pages/api/robots.txt (Next.js)exportdefaultfunctionrobots(req, res) { res.setHeader(‘Content-Type’, ‘text/plain’); res.send(` User-agent: * Allow: / Sitemap: ${process.env.SITE_URL}/sitemap.xml `);}
🔗 4. Advanced Internal Linking & Canonicalization
Problem:
Without WordPress’s theme system, links and canonical URLs can become inconsistent.
Solutions:
- ✅ Use absolute, clean URLs
Storepermalinkfrom WordPress (post.link) and use it as the canonical URL. - ✅ Enforce trailing slashes (or not) consistently
Redirect mismatches via middleware or CDN rules. - ✅ Audit internal links
Use tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to ensure:- No broken links
- Logical site architecture (hub-and-spoke, silos)
- Contextual anchor text from WordPress content
💡 Leverage WordPress’s
_linksin REST API responses to discover related content programmatically.
📸 5. Image & Media SEO Optimization
Problem:
Images from WordPress Media Library may be unoptimized or lack proper SEO attributes.
Solutions:
- ✅ Use modern image formats (WebP, AVIF) via:
- Next.js
next/imagewith WordPress source - Cloudinary or Imgix as an image optimization layer
- Next.js
- ✅ Preserve alt text & captions
Ensure your REST API exposes: json
- 1234⌄”featured_media”: { “alt_text”: “Descriptive alt text from WordPress”, “source_url”: “https://…”}
- ✅ Lazy-load + responsive images
Usesrcsetandsizesattributes generated from WordPress image metadata.
⚡ 6. Core Web Vitals & Performance Optimization
Why it matters:
Page experience (LCP, FID, CLS) is a confirmed Google ranking factor.
Headless advantages:
- ✅ Faster TTFB: Deploy frontend on Vercel/Netlify with edge caching.
- ✅ Code splitting: Only load necessary JS per route.
- ✅ Preload critical resources: Use
<link rel="preload">for fonts, hero images.
Monitor:
- Use Lighthouse CI in your build pipeline.
- Track real-user metrics via CrUX Dashboard or Google Search Console > Core Web Vitals.
🌐 7. Multilingual & International SEO (if applicable)
If your headless WordPress supports multiple languages (via WPML, Polylang, or custom fields):
- ✅ Expose hreflang data via REST API
- ✅ Render
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="x" href="..." />in<head> - ✅ Use language-specific sitemaps
Example:
jsx
1
2
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”en” href=”https://example.com/en/post” />
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”es” href=”https://example.com/es/post” />
🔒 8. Security & Indexing Control
- ✅ Block admin/API routes from indexing:
Add torobots.txt:
- 12Disallow: /wp-json/Disallow: /wp-admin/
- ✅ Prevent duplicate content:
Ensure WordPress doesn’t serve public frontend if you’re using it headlessly. Redirect all theme requests to your headless app or return 404/410.
🛠️ Recommended Tools for Headless WordPress SEO
| Purpose | Tool |
| API Enhancement | WPGraphQL, ACF to REST API, Custom REST Endpoints |
| Frontend Framework | Next.js (best SSR/SSG + SEO support) |
| Sitemap Generation | next-sitemap, nuxt-simple-sitemap |
| Schema Markup | next-seo, vueuse/schema-org |
| Monitoring | Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, Lighthouse |
| Image Optimization | next/image, Cloudinary, imgix |
✅ Final Checklist for Headless WordPress SEO
- Content is SSR/SSG-rendered (not CSR-only)
- Dynamic meta tags pulled from WordPress (Yoast/ACF)
- Valid
sitemap.xmlandrobots.txt - Canonical URLs match WordPress permalinks
- Images optimized with proper
alttext - Core Web Vitals ≥ 90 (Lighthouse)
- Structured data implemented (validate via Rich Results Test)
- No duplicate content (WordPress frontend disabled)
- Fast global delivery (CDN + edge caching)
Bottom Line:
Headless WordPress removes SEO guardrails—but gives you unmatched control. By treating SEO as a first-class feature in your frontend architecture, you can build sites that outperform traditional WordPress in speed, scalability, and search visibility.
The key: Intentional design, not automation. You’re not losing SEO—you’re upgrading to a more powerful, developer-centric model.
Conclusion:
A headless CMS is not bad for SEO—it’s a matter of implementation. With thoughtful architecture and attention to SEO fundamentals, headless systems can outperform traditional CMS setups in speed, flexibility, and search visibility.
Lastly, some believe that Headless CMSs are incompatible with popular SEO plugins and tools. While this might be the case out-of-the-box, many plugins, such as Yoast SEO, have developed headless solutions or can be adapted to work with a Headless CMS, ensuring that you can still leverage their capabilities.
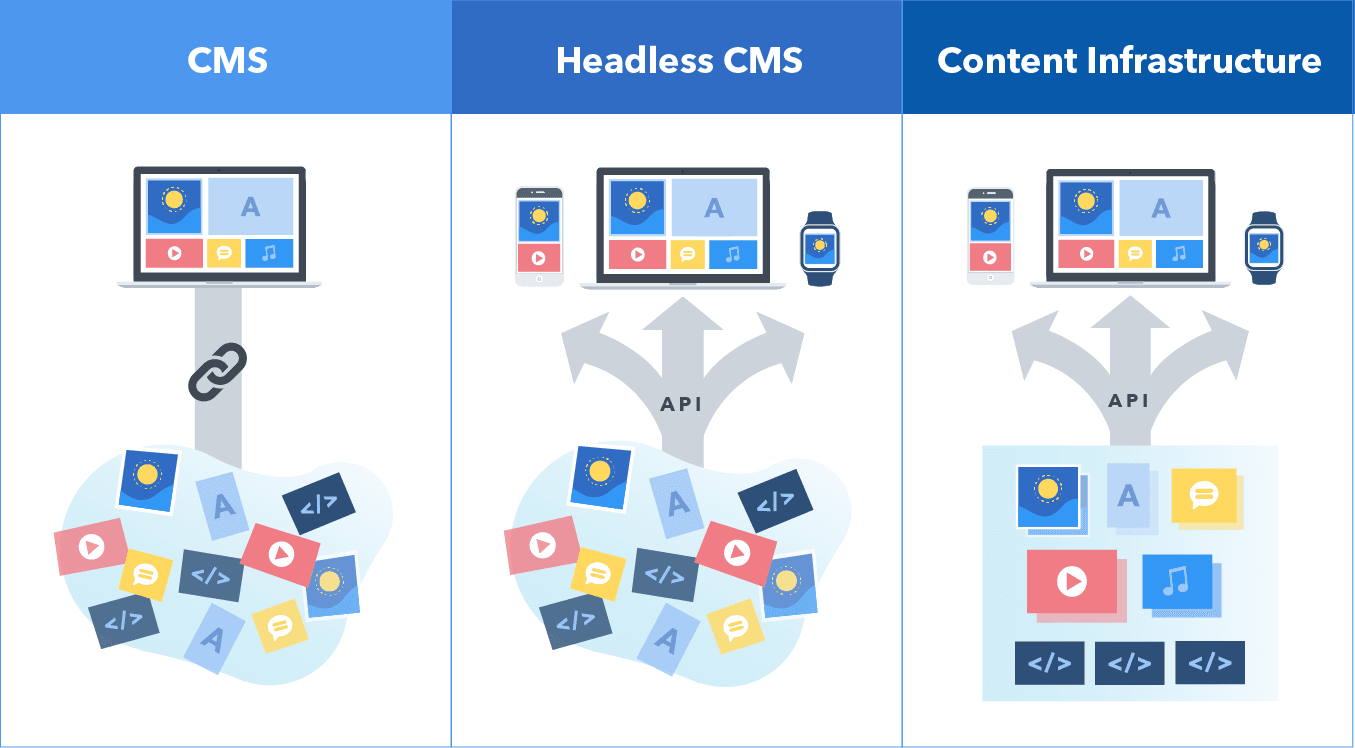
Headless CMS vs. Traditional CMS: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the differences between a Headless CMS and a Traditional CMS is crucial for determining which system best suits your SEO needs. Here’s a breakdown of how these two systems compare:
Traditional CMS:
- Coupled Architecture: Combines the content management backend with the front-end delivery layer, making it easier to implement SEO features.
- Ease of Use: Often includes built-in SEO tools and plugins, which simplify the optimization process for non-technical users.
- Limited Flexibility: The tightly integrated architecture can limit customization and the ability to deliver content across multiple platforms.
Headless CMS:
- Decoupled Architecture: Separates the backend from the front-end, allowing for greater flexibility and scalability.
- Customization and Performance: Offers advanced customization options and improved performance through faster content delivery.
- Technical Expertise Required: Requires a deeper understanding of web development and SEO to implement effectively.
Choosing between a Headless CMS and a Traditional CMS depends on your specific needs and resources. If you require extensive customization and multi-platform delivery, a Headless CMS may be the better option. However, if ease of use and built-in SEO features are a priority, a Traditional CMS might be more suitable.
Advanced SEO Strategies for Headless WordPress Sites
For those using WordPress as a Headless CMS, implementing advanced SEO strategies is essential to optimize your site for search engines. Here are some techniques to consider:
- Server-Side Rendering: Implementing server-side rendering can help search engines crawl and index your content more effectively, as it allows them to access the fully rendered page.
- Utilize Structured Data: Incorporating structured data helps search engines understand the context of your content, which can improve visibility in search results.
- API Optimization: Ensure that your APIs are optimized for performance, as slow API response times can negatively impact SEO.
- Dynamic Sitemaps: Create dynamic sitemaps that update automatically as new content is added, ensuring that search engines are always aware of the most recent site changes.
- Implementing Prerendering Services: Using services like Prerender.io can help render pages for search engines, making JavaScript-heavy sites more SEO-friendly.
By focusing on these strategies, you can enhance the SEO performance of your Headless WordPress site, ensuring that it ranks well in search engine results.
How to Optimize Your Headless CMS for SEO
Optimizing a Headless CMS for SEO involves several key steps. Here’s a guide to help you get started:
- Conduct a Technical SEO Audit: Begin by assessing the current state of your Headless CMS to identify any technical issues that may hinder search engine crawling and indexing. Look for broken links, duplicate content, and ensure that your site is mobile-friendly.
- Implement Meta Tags and Headers: Ensure all pages include relevant meta tags and header tags. Although these elements are not automatically included in Headless CMSs, they are essential for conveying the content’s subject matter to search engines.
- Optimize URL Structure: Create clean and descriptive URLs that reflect the content’s hierarchy and keywords. This aids both users and search engines in understanding the page’s content.
- Focus on Content Delivery: Optimize how content is delivered via APIs to ensure fast load times and a seamless user experience. This may involve caching, API performance tuning, or using a content delivery network (CDN).
By taking these steps, you can ensure that your Headless CMS is fully optimized for SEO, helping you achieve better rankings and visibility.
Using Yoast SEO with Headless CMS: A Guide
Yoast SEO is a popular tool among WordPress users, but how does it integrate with a Headless CMS? Here’s a guide on leveraging Yoast SEO in a headless setup:
- API Integration: Yoast SEO can be integrated into your Headless CMS via APIs. This allows you to access Yoast’s powerful SEO capabilities even in a decoupled environment.
- Custom Endpoint Development: To use Yoast effectively, develop custom endpoints that allow Yoast data to be accessed and utilized in your Headless CMS.
- Utilize Yoast’s REST API: The Yoast SEO plugin offers REST API endpoints that provide access to SEO metadata, which can be incorporated into your site’s API calls.
- Implement Yoast Suggestions: Use Yoast’s analysis and suggestions to improve content readability, keyword density, and other SEO factors, ensuring your content is optimized before publishing.
By following this guide, you can take advantage of Yoast SEO’s features, even when using a Headless CMS, to enhance your site’s search engine performance.
Best Practices for Implementing Headless CMS SEO
When implementing SEO in a Headless CMS, adhering to best practices is crucial. Here are some strategies to ensure success:
- Consistent Content Updates: Regularly update your content to keep it fresh and relevant. Search engines favor sites that frequently provide new information.
- Seamless User Experience: Ensure that the user experience is consistent across all devices and platforms. A seamless experience can lead to higher engagement rates, which positively impacts SEO.
- Monitor and Analyze Performance: Use analytics tools to monitor your site’s performance and identify areas for improvement. Track metrics such as load times, bounce rates, and user engagement.
- Leverage Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): Consider using PWAs to enhance user experience and improve load times, both of which are important for SEO.
- Stay Informed: SEO is constantly evolving, so staying informed about the latest trends and updates is essential. Regularly review SEO publications and attend industry conferences.
By following these best practices, you can effectively implement SEO strategies that are tailored to the unique architecture of a Headless CMS.
Case Studies: Successful Headless CMS SEO Implementations
To illustrate the potential of Headless CMS SEO, let’s explore some case studies of successful implementations:
- The New York Times: By adopting a Headless CMS, The New York Times was able to improve site speed and deliver content more efficiently across various platforms, resulting in enhanced SEO performance and increased reader engagement.
- Nike: Nike utilized a Headless CMS to provide a seamless omnichannel experience for its users. By integrating their e-commerce site with various digital touchpoints, they achieved better SEO rankings and higher conversion rates.
- Spotify: Spotify’s use of a Headless CMS allowed them to deliver personalized content to users across multiple devices. This approach not only improved user experience but also boosted their visibility in search engine results.
These examples demonstrate how organizations can leverage a Headless CMS to achieve impressive results in SEO and user engagement by focusing on performance, flexibility, and innovation.
Yoast SEO headless
Using Yoast SEO in a headless WordPress setup requires extra steps—because Yoast is built for traditional (coupled) WordPress sites where PHP renders the frontend. In a headless architecture, WordPress acts only as a content backend, and the frontend (e.g., Next.js, React, Vue) is built separately—so Yoast’s auto-generated meta tags, Open Graph data, and schema won’t appear automatically.
But yes—you can still use Yoast SEO with headless WordPress. Here’s how to do it correctly and effectively.
✅ Why Use Yoast in Headless WordPress?
- Content editors get Yoast’s familiar SEO analysis, readability checks, and snippet previews.
- Yoast stores structured SEO metadata (title, meta description, OG tags, focus keyphrase, canonical URL, etc.).
- You can expose this data via the REST API or GraphQL and render it on your headless frontend.
🔧 Step-by-Step: Expose Yoast SEO Data in Headless Mode
1. Install Yoast SEO (Free or Premium)
Standard installation in your WordPress admin.
2. Expose Yoast Data via REST API
By default, Yoast does not expose its SEO fields in the WordPress REST API. You need to enable this.
Option A: Use a Plugin (Recommended for Simplicity)
- WP REST API Controller
Lets you expose custom fields (including Yoast’s) via the REST API. - Yoast SEO: REST API (Unofficial, but widely used)
Adds Yoast SEO fields directly to REST API responses. After activation, your post response includes:
"yoast_head": "<!-- All Yoast-generated HTML tags -->",
"yoast_meta": {
"title": "Your SEO Title",
"description": "Your meta description",
"og_title": "Open Graph Title",
"og_description": "...",
"canonical": "https://example.com/post",
"focus_keyphrase": "headless wordpress seo"
}⚠️ Avoid using
yoast_headdirectly—it includes<meta>,<title>, and<script>tags meant for PHP rendering. Parse structured data instead.
Option B: Add Custom Code to functions.php
Add this to your theme’s functions.php or a custom plugin:
// Add Yoast SEO data to REST API responses
function add_yoast_to_rest_api($data, $post, $context) {
if (class_exists('WPSEO_Meta')) {
$focus_kw = WPSEO_Meta::get_value('focuskw', $post->ID);
$meta_desc = WPSEO_Meta::get_value('metadesc', $post->ID);
$canonical = WPSEO_Meta::get_value('canonical', $post->ID);
// Get title (use snippet preview logic or fallback)
$title = WPSEO_Meta::get_value('title', $post->ID);
if (empty($title)) {
$title = get_bloginfo('name') . ' - ' . $post->post_title;
}
$data->data['yoast_seo'] = [
'focus_keyphrase' => $focus_kw,
'meta_description' => $meta_desc,
'canonical' => $canonical ?: get_permalink($post->ID),
'title' => $title,
'og_title' => WPSEO_OpenGraph::get_instance()->get_title($post->ID),
'og_description' => WPSEO_OpenGraph::get_instance()->get_description($post->ID),
];
}
return $data;
}
add_filter('rest_prepare_post', 'add_yoast_to_rest_api', 10, 3);
add_filter('rest_prepare_page', 'add_yoast_to_rest_api', 10, 3);This gives you clean, structured SEO data—not raw HTML.
3. Fetch & Render SEO Data in Your Headless Frontend
Example: Next.js Page
// pages/posts/[slug].js
import Head from 'next/head';
import { getPostBySlug } from '../lib/api';
export default function Post({ post }) {
const seo = post.yoast_seo;
return (
<>
<Head>
<title>{seo.title}</title>
<meta name="description" content={seo.meta_description} />
<link rel="canonical" href={seo.canonical} />
{/* Open Graph */}
<meta property="og:title" content={seo.og_title || seo.title} />
<meta property="og:description" content={seo.og_description || seo.meta_description} />
<meta property="og:type" content="article" />
{/* Optional: JSON-LD Schema */}
<script type="application/ld+json">
{JSON.stringify(generateArticleSchema(post))}
</script>
</Head>
<article>
<h1>{post.title.rendered}</h1>
<div dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: post.content.rendered }} />
</article>
</>
);
}⚠️ Common Pitfalls & Fixes
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Yoast data missing in API | Use a plugin or custom code to expose it |
| Duplicate meta tags | Don’t use yoast_head—parse fields manually |
| Missing Open Graph images | Expose og_image via custom code or ACF |
| Focus keyphrase not used | Pull it from API and use for internal linking or analytics |
| No breadcrumbs | Generate them from WordPress categories/tags or use Yoast’s breadcrumb schema (expose via API) |
🔄 Alternative: Use WordPress as a Headless CMS Without Yoast
If you don’t want to rely on Yoast:
- Use ACF (Advanced Custom Fields) to create custom SEO fields (title, description, etc.)
- Expose them via REST API or WPGraphQL
- Gives more control but loses Yoast’s content analysis
✅ Best of both worlds: Use Yoast for editorial guidance + ACF for structured frontend data.
🧪 Validate Your Implementation
- Check API response:
Visityoursite.com/wp-json/wp/v2/posts/123— do you seeyoast_seo? - View page source:
Ensure<title>and<meta name="description">reflect Yoast settings. - Test with Google Rich Results Test
Verify structured data (if implemented). - Use Facebook Sharing Debugger
Confirm Open Graph tags render correctly.
✅ Summary: Yoast SEO + Headless WordPress = ✅ (With Setup)
| What Works | What Doesn’t |
|---|---|
| ✅ SEO analysis for editors | ❌ Auto-rendered meta tags (no PHP frontend) |
| ✅ Storing SEO metadata | ❌ Social previews in WordPress admin may not reflect headless URL |
| ✅ Exposing data via API | ❌ Readability/SEO scores don’t affect frontend (but still useful for content) |
🔑 Key: Treat Yoast as a content-editing and metadata-storage tool, not a frontend renderer.
By exposing Yoast’s structured SEO data and rendering it intelligently in your headless frontend, you get the best of both worlds:
- Editor-friendly SEO guidance (Yoast)
- High-performance, modern UX (React/Next.js/etc.)
Just remember: You’re in control now—SEO doesn’t happen automatically. But with this approach, it can be even better than traditional WordPress.
Conclusion: The Future of Headless CMS and SEO
As digital marketers, we must remain adaptable and forward-thinking. The future of Headless CMS and SEO is promising, with the potential to revolutionize how we approach content delivery and optimization. While challenges exist, the benefits of increased flexibility, performance, and scalability make Headless CMSs a compelling choice for many.
As we look ahead, it will be essential to continue exploring innovative SEO strategies and tools that can enhance the capabilities of Headless CMSs. By doing so, we can ensure that our digital marketing efforts remain effective and competitive in an ever-changing landscape.
If you’re considering transitioning to a Headless CMS, or are already using one and looking to improve your SEO strategy, now is the time to act. Embrace the potential of this technology and position your brand for success in the digital age.
For further insights and personalized guidance on implementing Headless CMS SEO strategies, feel free to reach out to our team of experts. We’re here to help you navigate the complexities of this exciting technology and achieve your digital marketing goals.